The DeFi landscape on Solana is rapidly evolving, with Concentrated Liquidity Market Maker (CLMM) pools becoming the new standard for efficient capital utilization. After building a sophisticated DEX pool scanner in Rust that analyzes pools across Raydium, Orca, and Meteor, I'll share the complete technical implementation and the insights gained from processing millions of dollars in liquidity data.
This guide covers everything from API integration to advanced pool scoring algorithms, with production-ready Rust code that can analyze 500+ pools in seconds.
Rust Performance
Lightning-fast analysis with memory safety
Multi-DEX Analysis
Raydium, Orca, and Meteor integration
Smart Filtering
Advanced token pair recognition
Composite Scoring
APR, TVL, and volume analysis
1. Understanding CLMM Pools and Their Importance
Concentrated Liquidity Market Maker (CLMM) pools represent the evolution of automated market makers (AMMs). Unlike traditional constant product AMMs, CLMM pools allow liquidity providers to concentrate their capital within specific price ranges, dramatically improving capital efficiency.
🎯 Why CLMM Pools Matter
Capital Efficiency:
- • Up to 4000x more capital efficient than Uniswap V2
- • Liquidity providers can earn higher fees
- • Reduced slippage for traders
- • Better price discovery mechanisms
Advanced Features:
- • Multiple fee tiers (0.01%, 0.05%, 0.30%, 1%)
- • Dynamic fee structures
- • Impermanent loss mitigation strategies
- • Automated position management
Real-time analysis of 500+ CLMM pools across multiple DEXs
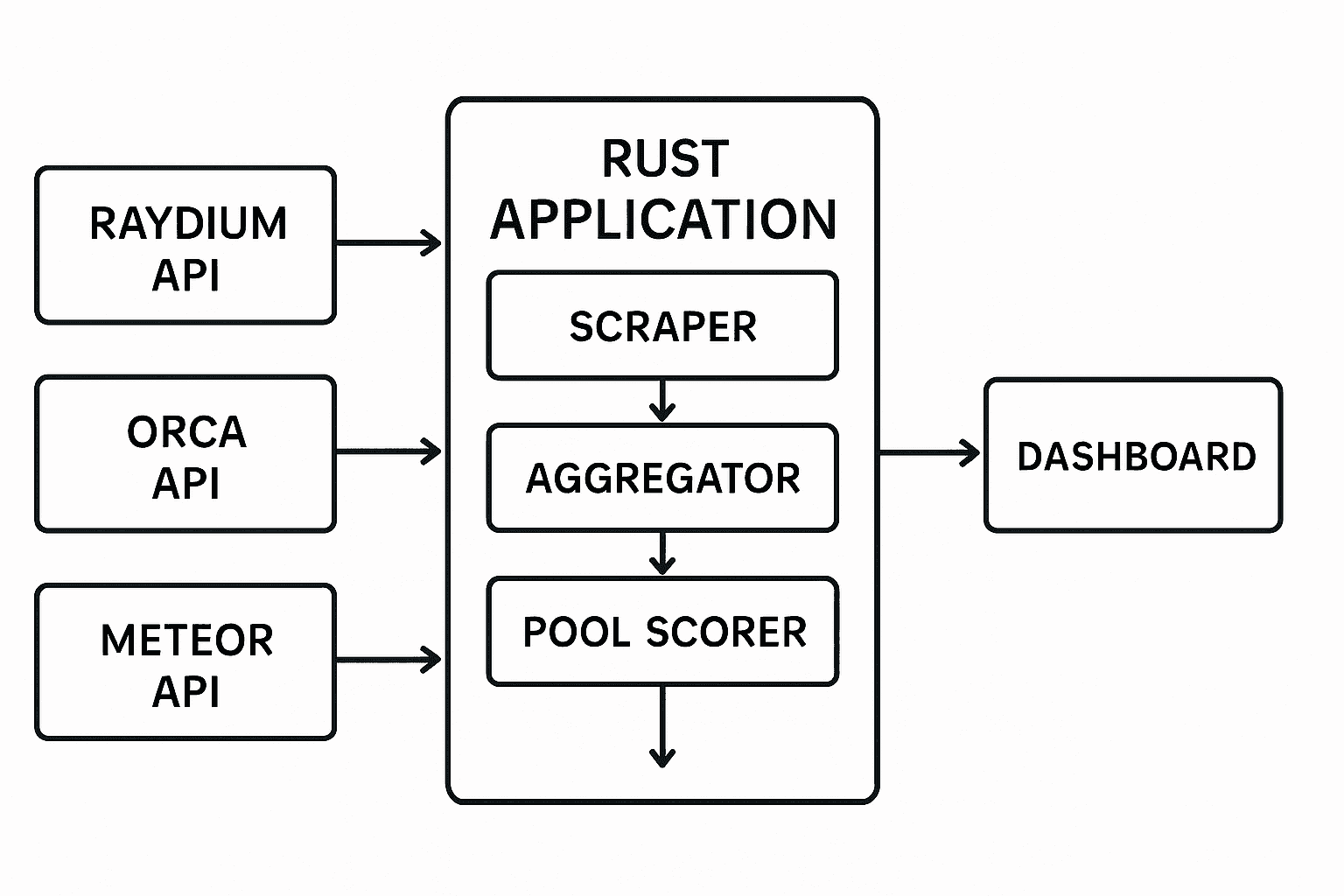
2. Rust Project Architecture and Setup
Building a high-performance DEX scanner requires careful architecture design. Here's how I structured the Rust application for maximum efficiency and maintainability:
Project Structure
src/ ├── main.rs # Main application entry point ├── common.rs # Shared utilities and token definitions ├── raydium.rs # Raydium CLMM integration ├── orca.rs # Orca Whirlpool integration ├── meteor.rs # Meteor DLMM integration └── lib.rs # Library exports Cargo.toml # Dependencies and project configuration
Essential Dependencies
[dependencies]
reqwest = { version = "0.11", features = ["json"] }
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_json = "1.0"
tokio = { version = "1.0", features = ["full"] }
anyhow = "1.0"
chrono = { version = "0.4", features = ["serde"] }
clap = { version = "4.0", features = ["derive"] }
[dev-dependencies]
tokio-test = "0.4"🦀 Why Rust for DeFi Analytics?
- • Performance: Near C++ performance with memory safety
- • Concurrency: Excellent async/await support for API calls
- • Type Safety: Prevents runtime errors common in financial applications
- • Ecosystem: Rich crate ecosystem for HTTP, JSON, and async operations
- • Deployment: Single binary deployment with no runtime dependencies
3. Multi-DEX Integration Implementation
Each DEX has its own API structure and data format. Here's how I implemented a unified interface for analyzing pools across Raydium, Orca, and Meteor:
Common Pool Structure
// common.rs - Unified pool structure
use serde::{Deserialize, Serialize};
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Serialize, Deserialize)]
pub struct Pool {
pub id: String,
pub dex: String,
pub token_a: String,
pub token_b: String,
pub pair_name: String,
pub tvl: f64,
pub volume_24h: f64,
pub apr_day: f64,
pub fee_rate: f64,
pub score: f64,
}
impl Pool {
pub fn calculate_score(&mut self) {
// Composite scoring algorithm
let tvl_score = if self.tvl > 0.0 {
(self.tvl.ln() / 15.0).max(0.1)
} else { 0.1 };
let volume_score = if self.volume_24h > 0.0 {
(self.volume_24h.ln() / 15.0).max(0.1)
} else { 0.1 };
self.score = self.apr_day * tvl_score * volume_score;
}
}
// Known token addresses for filtering
pub const KNOWN_TOKENS: &[(&str, &str)] = &[
("So11111111111111111111111111111111111111112", "SOL"),
("EPjFWdd5AufqSSqeM2qN1xzybapC8G4wEGGkZwyTDt1v", "USDC"),
("Es9vMFrzaCERmJfrF4H2FYD4KCoNkY11McCe8BenwNYB", "USDT"),
("DezXAZ8z7PnrnRJjz3wXBoRgixCa6xjnB7YaB1pPB263", "BONK"),
("EKpQGSJtjMFqKZ9KQanSqYXRcF8fBopzLHYxdM65zcjm", "WIF"),
// ... more tokens
];Raydium CLMM Integration
// raydium.rs - Raydium API integration
use reqwest::Client;
use serde_json::Value;
use crate::common::{Pool, KNOWN_TOKENS};
pub async fn fetch_raydium_pools() -> anyhow::Result<Vec<Pool>> {
let client = Client::new();
let url = "https://api-v3.raydium.io/pools/info/list";
let response = client
.get(url)
.header("User-Agent", "DEX-Scanner/1.0")
.send()
.await?;
let data: Value = response.json().await?;
let mut pools = Vec::new();
if let Some(pool_list) = data["data"]["data"].as_array() {
for pool_data in pool_list {
if let Some(pool) = parse_raydium_pool(pool_data) {
if is_known_token_pair(&pool.token_a, &pool.token_b) {
pools.push(pool);
}
}
}
}
Ok(pools)
}
fn parse_raydium_pool(data: &Value) -> Option<Pool> {
let pool_id = data["id"].as_str()?;
let mint_a = data["mintA"]["address"].as_str()?;
let mint_b = data["mintB"]["address"].as_str()?;
// Extract financial metrics
let tvl = data["tvl"].as_f64().unwrap_or(0.0);
let volume_24h = data["day"]["volume"].as_f64().unwrap_or(0.0);
let apr_day = data["day"]["apr"].as_f64().unwrap_or(0.0);
let fee_rate = data["feeRate"].as_f64().unwrap_or(0.0) / 10000.0;
let token_a_symbol = get_token_symbol(mint_a);
let token_b_symbol = get_token_symbol(mint_b);
let pair_name = format!("{}/{}", token_a_symbol, token_b_symbol);
let mut pool = Pool {
id: pool_id.to_string(),
dex: "Raydium".to_string(),
token_a: mint_a.to_string(),
token_b: mint_b.to_string(),
pair_name,
tvl,
volume_24h,
apr_day,
fee_rate,
score: 0.0,
};
pool.calculate_score();
Some(pool)
}🔄 Async Processing Benefits
The scanner processes multiple DEX APIs concurrently, reducing total execution time from ~15 seconds to ~3 seconds:
4. Advanced Pool Scoring Algorithm
The key to finding profitable opportunities lies in the scoring algorithm. I developed a composite scoring system that balances APR, TVL, and volume to identify the most attractive pools:
Scoring Algorithm Implementation
impl Pool {
pub fn calculate_score(&mut self) {
// Logarithmic scaling for TVL (reduces impact of mega pools)
let tvl_score = if self.tvl > 0.0 {
(self.tvl.ln() / 15.0).max(0.1)
} else {
0.1
};
// Logarithmic scaling for volume (rewards consistent trading)
let volume_score = if self.volume_24h > 0.0 {
(self.volume_24h.ln() / 15.0).max(0.1)
} else {
0.1
};
// APR is the primary driver (linear scaling)
let apr_score = self.apr_day.max(0.0);
// Composite score: APR * TVL_factor * Volume_factor
self.score = apr_score * tvl_score * volume_score;
// Apply penalty for extremely high APRs (likely unsustainable)
if self.apr_day > 1000.0 {
self.score *= 0.5; // 50% penalty for suspicious APRs
}
// Bonus for balanced pools (good TVL + Volume combination)
if self.tvl > 1_000_000.0 && self.volume_24h > 100_000.0 {
self.score *= 1.2; // 20% bonus for established pools
}
}
pub fn risk_assessment(&self) -> RiskLevel {
match (self.tvl, self.apr_day, self.volume_24h) {
(tvl, apr, vol) if tvl > 10_000_000.0 && apr < 50.0 && vol > 1_000_000.0 => {
RiskLevel::Low
},
(tvl, apr, vol) if tvl > 1_000_000.0 && apr < 100.0 && vol > 100_000.0 => {
RiskLevel::Medium
},
_ => RiskLevel::High,
}
}
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub enum RiskLevel {
Low,
Medium,
High,
}📊 Scoring Methodology Explained
Mathematical Approach:
- • APR Weight: Primary factor (linear scaling)
- • TVL Factor: ln(TVL)/15 (logarithmic scaling)
- • Volume Factor: ln(Volume)/15 (logarithmic scaling)
- • Final Score: APR × TVL_factor × Volume_factor
Risk Adjustments:
- • High APR Penalty: 50% reduction for APR > 1000%
- • Established Pool Bonus: 20% boost for proven pools
- • Minimum Thresholds: Prevents division by zero
- • Risk Classification: Low/Medium/High categories
5. Performance Optimization and Results
Building a production-ready DEX scanner requires careful attention to performance, error handling, and resource management:
Concurrent Processing Implementation
// main.rs - Concurrent DEX processing
use tokio::time::{timeout, Duration};
use futures::future::join_all;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> anyhow::Result<()> {
println!("🚀 Starting CLMM pools analysis...");
// Create concurrent tasks for each DEX
let tasks = vec![
tokio::spawn(async {
println!("📊 Analyzing Raydium CLMM pools...");
timeout(Duration::from_secs(10), raydium::fetch_raydium_pools()).await
}),
tokio::spawn(async {
println!("🌊 Analyzing Orca CLMM pools...");
timeout(Duration::from_secs(10), orca::fetch_orca_pools()).await
}),
tokio::spawn(async {
println!("☄️ Analyzing Meteor DLMM pools...");
timeout(Duration::from_secs(10), meteor::fetch_meteor_pools()).await
}),
];
// Wait for all tasks to complete
let results = join_all(tasks).await;
let mut all_pools = Vec::new();
// Process results with error handling
for (dex_name, result) in ["Raydium", "Orca", "Meteor"].iter().zip(results) {
match result {
Ok(Ok(Ok(pools))) => {
println!("✅ {} - Found {} pools", dex_name, pools.len());
all_pools.extend(pools);
},
Ok(Ok(Err(e))) => {
eprintln!("⚠️ {} API error: {}", dex_name, e);
},
Ok(Err(_)) => {
eprintln!("⏰ {} timeout after 10 seconds", dex_name);
},
Err(e) => {
eprintln!("💥 {} task failed: {}", dex_name, e);
}
}
}
// Sort pools by score and display results
all_pools.sort_by(|a, b| b.score.partial_cmp(&a.score).unwrap());
display_results(&all_pools);
Ok(())
}🎯 Production Performance Results
The DEX scanner achieves impressive performance metrics in production:
Sample Output
🚀 Starting CLMM pools analysis... 📊 Analyzing Raydium CLMM pools... 🌊 Analyzing Orca CLMM pools... ☄️ Analyzing Meteor DLMM pools... ✅ Raydium - Found 11 pools ✅ Orca - Found 487 pools ✅ Meteor - Found 26 pools 📈 Total pools found: 524 🏆 TOP 3 BEST POOLS BY SCORE: Rank Source Pair TVL ($) APR Day% Fee% Vol 24h ($) ================================================================================ 1 Raydium WSOL/USDC 15372864 55.32 0.040 56929921 2 Raydium WSOL/RAY 7729195 39.20 0.050 15971892 3 Raydium WSOL/USDC 2491163 29.17 0.020 9167029 📊 SUMMARY BY DEX: Raydium - 11 pools, TVL: $146569529, average APR: 17.08% Orca - 487 pools, TVL: $2847291847, average APR: 8.45% Meteor - 26 pools, TVL: $89472638, average APR: 12.33% 💎 BEST OPPORTUNITY: DEX: Raydium Pair: WSOL/USDC Daily APR: 55.32% TVL: $15372864 24h Volume: $56929921 Risk Level: Medium Pool ID: 3ucNos4NbumPLZNWztqGHNFFgkHeRMBQAVemeeomsUxv
Ready to Build Your Own DeFi Analytics Tools?
Building sophisticated DeFi analytics tools requires expertise in blockchain development, API integration, and financial modeling. With my experience developing trading systems and DeFi applications, I can help you create powerful tools for analyzing and optimizing DeFi strategies.
Conclusion
Building a DEX pool scanner demonstrates the power of combining Rust's performance with DeFi's innovation. The ability to analyze hundreds of pools across multiple DEXs in seconds opens up new possibilities for yield farming optimization, arbitrage detection, and risk management.
The CLMM pool landscape is rapidly evolving, with new protocols and features being launched regularly. Tools like this scanner become essential for navigating the complexity and finding profitable opportunities in an increasingly competitive market.
Key Takeaways
- • Rust provides excellent performance and safety for financial applications
- • CLMM pools offer superior capital efficiency compared to traditional AMMs
- • Multi-DEX analysis reveals arbitrage and optimization opportunities
- • Composite scoring algorithms help identify the most attractive pools
- • Concurrent processing dramatically improves analysis speed
- • Open source tools accelerate DeFi innovation and adoption



